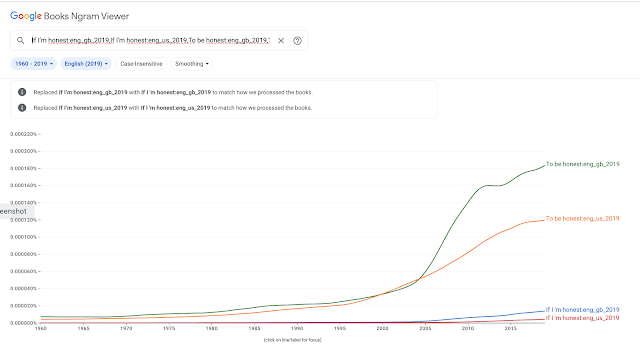
That last bit was news to me. I import A.1. from
the States because I love it so. (I find it spicier and less treacly than HP sauce. It's also much darker.) In the UK, I've only ever seen it in
Fortnum and Mason (extremely chichi shop), where they charged in the double digits for a bottle, apparently imported from the US. But A.1. (in some formulation) may still be being made in the UK for export to Asia! (The most recent reference to this I've found is 2018.)
Back to brown sauce. The OED definition has not been updated since 1888, and it has only the French-cuisine inspired meaning, akin to gravy: "A brown-coloured savoury sauce, esp. one made with browned fat and flour." When I was a(n American) child in the 1970s–80s learning about cooking, I learned this among other sauce terms—though I can't say I've ever heard it in my adult life.
But brown sauce was another bit of my mother's terminology that didn't help when travel(l)ing: she'd talk about her Chinese food preferences in terms of preferring brown sauce over white sauce, and British Spouse didn't understand what she meant. But, she knew what she was talking about. Goodcooking.com has a story about a sauce master at a Chinese restaurant which includes (with recipes):
Two basic sauces are the brown sauce and white sauce. Brown sauce is mainly for meat dishes; beef, lamb, duck, yet he also used it in his Chendu Fish dish, to bind together moo shu and one of his tofu dishes. The white sauce was for fish and seafood, chicken and vegetable dishes. Other ingredients such as black beans, chili with garlic, preserved vegetable, ginger and garlic were added as items cooked and then his sauces were added, seconds before service to bind everything into a flavorful dish.
From the spelling of flavorful, we can guess that this Chinese restaurant was in the US, and from a little knowledge of Chinese food in the anglosphere, I would guess that (a) this might be based in some specific regional Chinese cuisine, and (b) the term is not much used in British Chinese cuisine. Having had a lot of Chinese takeaways/takeout in the US, UK and South Africa, I can report that even if you're ordering a dish of the same name (chicken in garlic sauce, sweet-and-sour pork, General Tso's chicken etc.), they are very different in different places. (Let's just say: my English family always makes a point of having Chinese food when we're in the US.) Yummly.co.uk has many recipes for Chinese brown sauce, but, despite the 'uk' in its URL, all the brown-sauce recipes I checked there have American terminology (cornstarch, scallions, chicken broth/bouillon etc.). If there were any urge to call Chinese sauce base brown in British English, it would probaby be blocked by the clash with the breakfasty condiment.
white sauce
White sauce has at least the following meanings:
- In (US, at least) Chinese cuisine, it's the opposite of brown sauce. (This site says it's typical of Cantonese cooking.)
- A sauce base made of "roux of butter and flour combined with milk or cream" (OED).
The OED's (2015 updated) entry includes only the last of these, which is often used in French cooking. It's also what my mother used as the opposite of
red sauce in Italian cooking, so
an Alfredo or similar.
Speaking of white sauces in Italian cooking—I grew up hating (AmE) lasagna/(BrE) lasagne because I couldn't stand the ricotta cheese. Well, it turns out, British people don't make lasagne with ricotta (nor do many in Italy). Instead it has a béchamel sauce. Meanwhile, I've outgrown my hatred of ricotta. Still, lasagn{a/e} is the last thing I'd order on any pasta menu.
Finally,
for the fun of it, a Venn diagram of sauces by
Zoe Laughlin, recently discussed on BBC Radio 4 and pointed out to me by one of my writing group pals:



















_by_Blake_Shelton.png)